Everything You Need to Know About Charging Up
Instead of gasoline, electric cars use electricity to charge. If you’re new to electric vehicles, you likely have some questions about charging—how and where it’s done and what it costs. We’ve got your answers. Charge at home, at work and on the road!e
The number of charging stations keeps increasing. Plus, charging is more convenient and faster than ever. There are more than 1,600 public charging outlets at over 600 charging stations in Oregon and 78,500 public charging outlets nationwide.
- Charge up to 80% of your battery capacity in 30 minutes (with DC fast charging).
- Drive 200+ miles per charge (depending on vehicle range).
- Find hundreds of public charging stations nearby with easy to use apps.
How Far Is Your Commute?
Most Americans commute under 32 miles a day round trip. Most electric cars now offer 200+ miles per charge. Even entry-level electric cars have a range of 80+ miles per charge.
Basics of Charging
Level 1
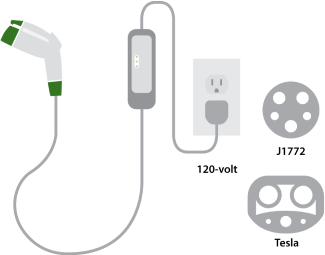
- Plug into a standard grounded, 120-volt outlet.
- All you need is the charging cable that comes with your car.
- Great for overnight charging at home.
- Available for PHEVs and BEVs.
Level 2
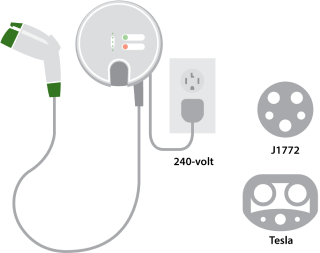
- Plug into a high-powered 240-volt outlet at a public or home charging station.
- Ideal for charging at home, at work or on the road.
- Fully recharge in just a few hours.
- Available for PHEVs and BEVs.
Level 3 DC Fast Charging
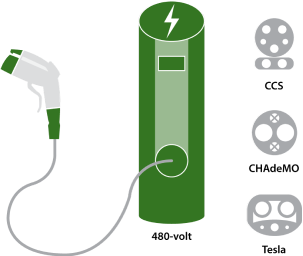
- Charge up in less than an hour.
- The CHAdeMO standard is used by most Japanese and Korean plug-in cars. The CCS Combo standard is used by most American and European plug-in cars.
- Tesla has a fast-charging network specific to its cars with a different plug shape.
- Available for some PHEVs and BEVs.
Charging at Home
In most cases, home charging is cheaper than public charging. You can plug your car right into a standard 120-v outlet (Level 1). For faster charging, you can install a home charger that uses the same high-powered 240 voltage as your washer, dryer or stove (Level 2).
The costs of home charging vary based on utility rates and time of use, but on average it costs $10 for 240 miles of charge. A home charging station costs between $300‒$1,000, plus installation.
Charging at Work
Car charging at the workplace is becoming more and more common, and some businesses will provide it if requested. Just ask—there are many reasons employers would consider EV charging.
